material of container
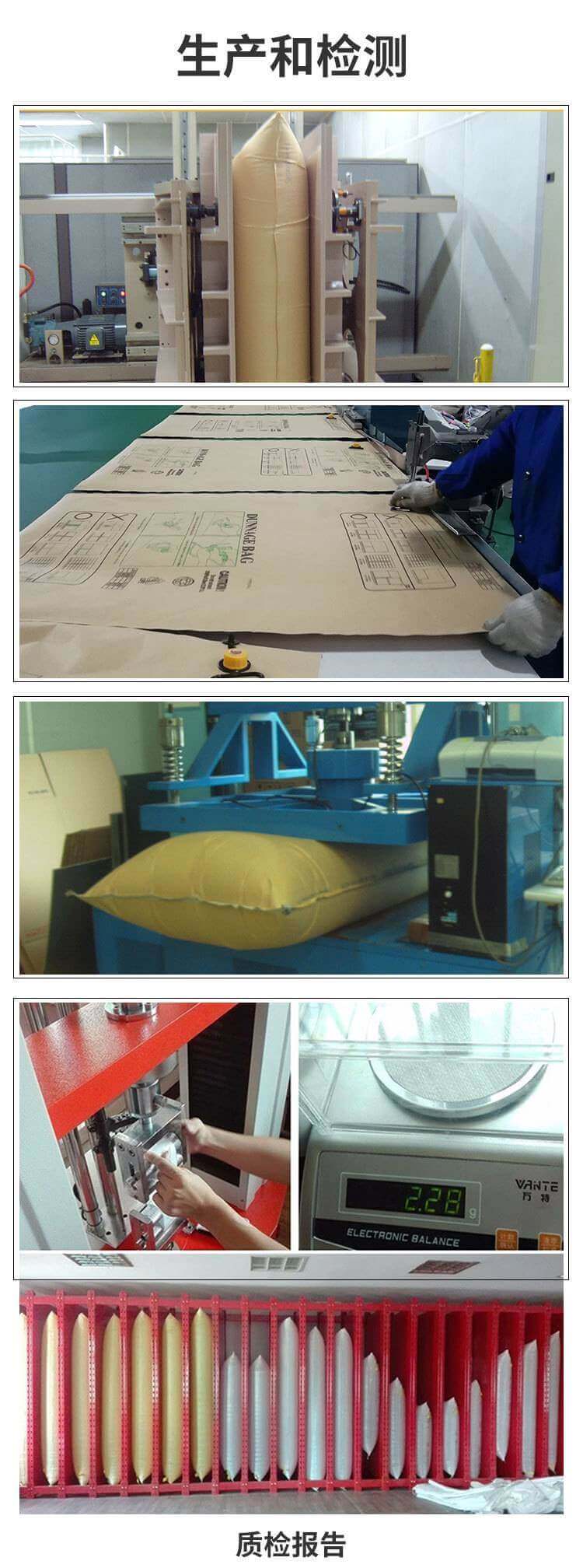





Container Materials: Types, Benefits, and Applications Containers are a crucial element of logistics and supply chain management, providing a means of transporting and storing goods efficiently. The material used to construct containers can vary, with several options available that offer different benefits and applications. Types of Container Materials Metal: Metal containers are typically made from steel or aluminum and are highly durable, resistant to corrosion, and able to withstand heavy weights. They are commonly used for transporting liquids, solids, and hazardous materials. Plastic: Plastic containers are lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to handle. They are suitable for a wide range of applications, including packaging, storage, and transportation. Plastic containers are also recyclable and can be定制ed to specific needs. Wood: Wooden containers are traditional and commonly used for storing and transporting dry goods. They are sturdy and can handle heavy weights, but require regular maintenance to prevent decay and splintering. Cardboard: Cardboard containers are primarily used for packaging and shipping items such as clothing, books, and small items. They are lightweight, recyclable, and cost-effective, but are not suitable for heavy loads or rough handling. Benefits of Container Materials Durability: Metal, plastic, and wood containers are highly durable, able to withstand rough handling and long-term storage. Cost-Effectiveness: Plastic and cardboard containers are generally more cost-effective than metal or wood containers, with lower material costs and ease of production. Recyclability: Plastic and cardboard containers are easily recyclable, reducing waste and environmental impact. Customizability: Container materials can be modified or customized to meet specific needs, such as adding handles, labels, or special coatings. Portability: Container materials should be lightweight and easy to handle for convenient transportation and storage. Applications of Container Materials Container materials are used for a wide range of applications, including: Shipping: Containers are essential for shipping goods worldwide, with different materials suitable for different types of goods. For example, metal containers are commonly used for shipping liquids or hazardous materials, while plastic containers are suitable for lightweight, non-hazardous items. Storage: Container materials are used for long-term or short-term storage of goods, with different materials suitable for different types of goods. For example, metal or plastic containers are suitable for storing dry goods, while wood or cardboard containers are commonly used for storing books or clothing. Packaging: Container materials are used for packaging goods to protect them during transportation or storage and to ensure they arrive intact. Plastic containers are commonly used for packaging consumer goods, while cardboard containers are suitable for packaging books or clothing. Logistics: Containers play a crucial role in logistics operations, providing a standardized means of transporting and storing goods worldwide. Containerization has made it possible to move goods efficiently across borders and oceans, reducing transportation costs and enhancing supply chain efficiency. In conclusion, container materials vary depending on the application and type of goods being transported or stored. Each material has unique benefits and characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications. When selecting a container material, it's important to consider the type of goods, transportation needs, cost constraints, and environmental factors to ensure the best possible solution is selected for efficient and sustainable logistics operations.







 wechat consulting
wechat consulting